On-Grid Solar System
On-Grid Solar System
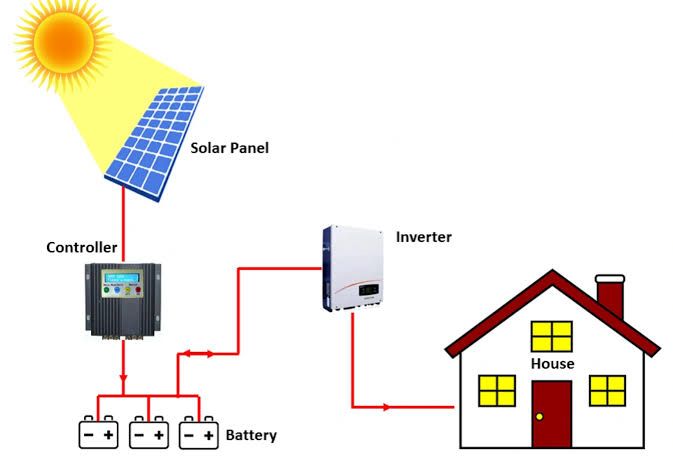
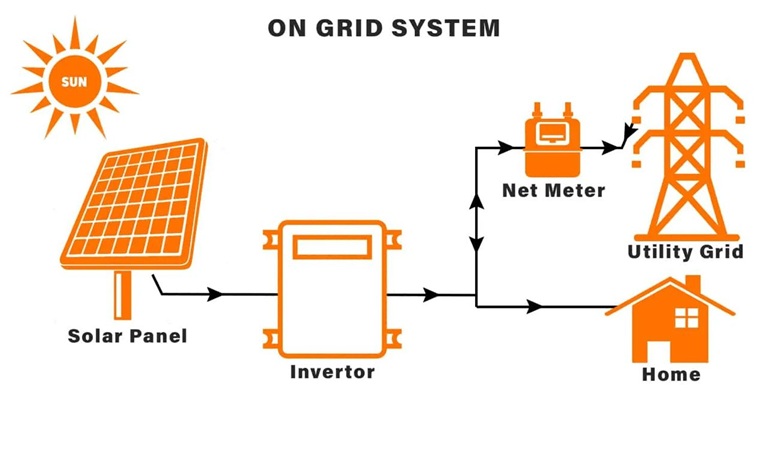
Overview: A grid-tied system that generates solar power and feeds excess energy back to the grid.
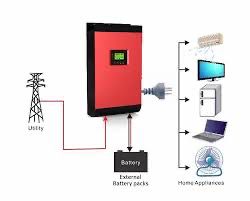
Key Features: No batteries required (though optional), net metering for surplus energy, reliant on the grid.
Advantages: Cost-effective, easy to scale, low maintenance.
Disadvantages: Dependent on grid availability; not functional during outages without battery backup.
Ideal For: Urban/suburban homes and businesses aiming to reduce electricity costs.